Central Coast Head and Neck Surgeons (CCHNS) care for all aspects of ear (otologic) problems from hearing loss to dizziness to infection. They are teamed with a skilled group of audiologists to assess hearing difficulties from newborns to adults. They also have advanced diagnostics to assess balance difficulties. Depending on the condition, treatments range from medical interventions to surgical intervention. The physicians of CCHNS provide the full spectrum of treatment options available including the latest microsurgical techniques to hearing amplification.
ENT Procedures
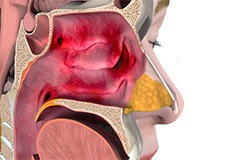
Sinus and Allergy Treatment/Surgery
It is defined as inflammation of the paranasal sinus cavities and can be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or fungi, or chronic irritation from allergies.
Thyroid Surgery
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in front of your neck just below the voice box (larynx). Thyroid surgery involves the removal of part or the whole thyroid gland.
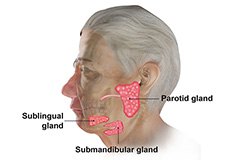
Salivary Gland Surgery
The purpose of saliva is to moisten the mouth, protect the teeth against bacteria and aid in the digestive process. Saliva is produced by 3 main salivary glands which include the parotids, submandibular and sublingual glands.
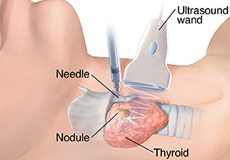
In Office Thyroid or Neck Ultrasound and Biopsies
The thyroid gland, located in front of the neck region is responsible for the production of thyroid hormones. These hormones control various body functions such as regulation of metabolism and body temperature.
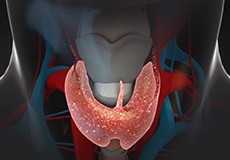
Management of Thyroid Disorders (Non-Surgical)
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in front of your neck just below the voice box (larynx). It secretes hormones that help regulate your body’s metabolism.
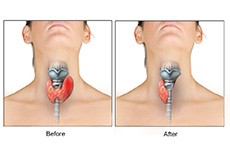
Thyroidectomy
Thyroid cancer is an abnormal growth of the cells of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck just below the voice box (larynx). Thyroid gland secretes hormones that help regulate the body’s metabolism and levels of calcium.
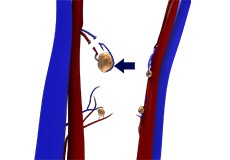
Parathyroidectomy
Parathyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of a part or complete parathyroid glands (which produce hormones that increase levels of calcium in blood). The treatment is indicated for patients with hyperparathyroidism (high levels of parathyroid hormone caused by a non-cancerous tumor).

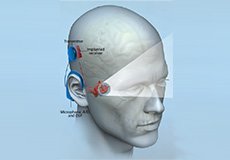
Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implantation is a procedure for the treatment of severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) in both children and adults. A cochlear implant is a device inserted into your ear to help in hearing.

Central Auditory Processing Evaluation and Treatment
Early diagnosis and intervention by a licensed audiologist can significantly improve quality of life by reducing the challenges associated with listening and understanding speech.
ENT Conditions
Hearing Loss/Aids
Hearing loss is a medical disorder that affects nearly 36 million adults in the United States. Impaired hearing may be caused by many things. Older people are the largest group affected by hearing loss.
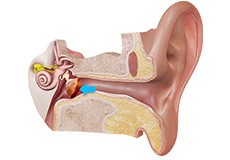
Cholesteatoma
An abnormal skin growth in the middle ear behind the eardrum is called cholesteatoma. Repeated infections and/or a tear or pulling inward of the eardrum can allow skin into the middle ear. Cholesteatomas often develop as cysts or pouches that shed layers of old skin, which build up inside the middle ear.
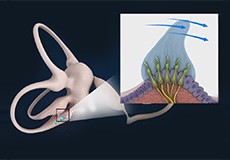
Dizziness / Vertigo
Dizziness can feel like you’re off balance or unsteady. Or it can feel like you’re lightheaded. Or it can feel like you or your surroundings are spinning or turning — also called “vertigo.” Just as there are different types of dizziness, there are different causes, including poor circulation, dehydration, medications, anxiety, brain injury, infection, allergy, neurological.
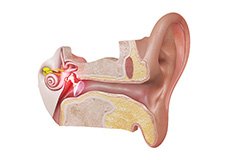
Ear Infection
Inflammation located in the middle ear, usually occurs when a cold, allergy, or upper respiratory infection, and the presence of bacteria or viruses lead to the accumulation of pus and mucus behind the eardrum, blocking the Eustachian tube.
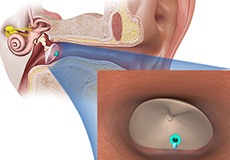
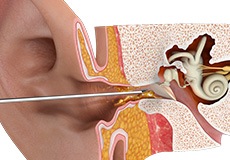
Earwax
Cerumen or earwax is healthy in normal amounts and serves as a self-cleaning agent with protective, lubricating, and antibacterial properties. Most of the time the ear canals are self-cleaning; that is, there is a slow and orderly migration of earwax and skin cells from the eardrum to the ear opening.
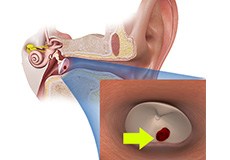
Eardrum Perforation (Tympanic Membrane Perforation)
A hole or rupture in the eardrum, a thin membrane that separates the ear canal and the middle ear, is called a perforated eardrum. The medical term for eardrum is tympanic membrane. A perforated eardrum can occur from trauma, infection, or chronic Eustachian tube disorders.

Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is a balance disorder caused by an abnormality found in a section of the inner ear called the labyrinth. Disorders of the fluids within the labyrinth can interfere with the normal balance and hearing signals between the inner ear and the brain, resulting in Meniere’s disease.
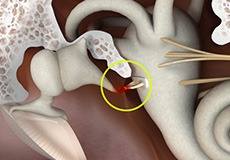
Otosclerosis
This is a disease of the otic capsule (bony labyrinth) in the ear, which is more prevalent in adults and characterized by formation of soft, vascular bone leading to progressive conductive hearing loss.
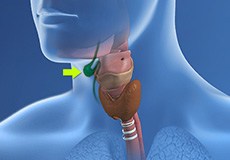
Thyroglossal Duct Cysts
Thyroglossal duct cysts are fluid-filled lumps or masses located just above the larynx (voice box) in front of the neck. They are formed from the leftover cells and tissues during formation of the thyroid gland at the time of embryonic development.
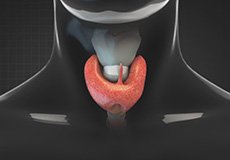
Hypothyroidism
The thyroid gland is located in front of the neck, just above the collarbone. It produces thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), necessary for using energy, staying warm and the proper functioning of various body parts such as the brain, heart and muscles.
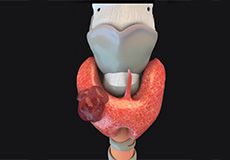
Thyroid Nodule
A thyroid nodule is defined as an abnormal or unusual growth of thyroid cells that occurs in the form of a lump in your thyroid gland. A thyroid nodule can be solid or fluid-filled and noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant) in nature.
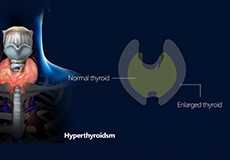
Hyperthyroidism
A Hyperthyroidism is defined as an abnormal or unusual growth of thyroid cells that occurs in the form of a lump in your thyroid gland. A Hyperthyroidism can be solid or fluid-filled and noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant) in nature.
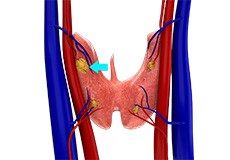
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a medical condition characterized by excess secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) into the bloodstream due to overactivity of one or more of your body’s parathyroid glands.
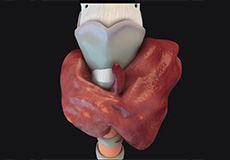
Multinodular Goiter
Goiter is defined as an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. Multinodular goiter is the presence of multiple nodules or bumps on an abnormally enlarged thyroid gland. These thyroid nodules are common, harmless, and mostly noncancerous.
ENT Anatomy
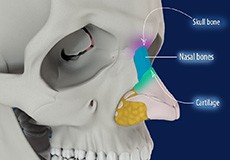
Anatomy of the Nose
The nasal passages serve as an entrance to the respiratory tract. These passages are lined by a moist mucous membrane with hair-like projections known as cilia which help collect dust, debris, and bacteria.
